Electrolytic cell diagram
Voltaic cells use a spontaneous chemical reaction to drive an electric current through an external circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis for the batteries that fuel electrolytic cell diagram society.
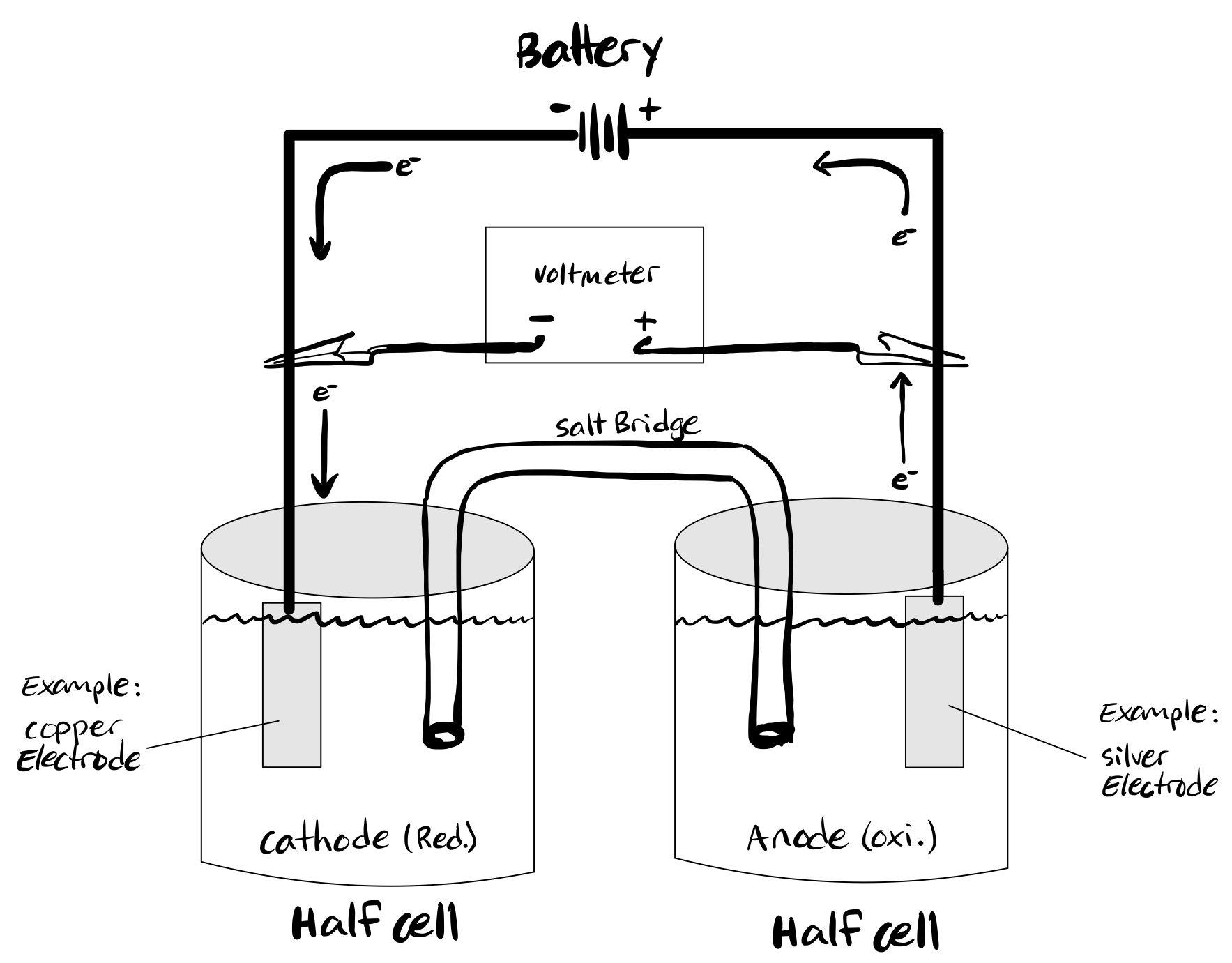
An electrolytic cell can be defined as an electrochemical device that uses electrical energy to facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells that can be used for the electrolysis of certain compounds. For example, water can be subjected to electrolysis with the help of an electrolytic cell to form gaseous oxygen and gaseous hydrogen. This is done by using the flow of electrons into the reaction environment to overcome the activation energy barrier of the non-spontaneous redox reaction. The electrolyte provides the medium for the exchange of electrons between the cathode and the anode.
Electrolytic cell diagram
A cell is a device capable of producing electrical energy from chemical reactions or employing electrical energy to bring about a chemical reaction. So, cells can be grouped into two major categories: one that produces electrical energy from chemical reactions and another that uses electrical energy to bring about a chemical reaction. While the former is called a galvanic or voltaic cell, the latter is an electrolytic cell. Both electrolytic and galvanic cells operate differently. The following table enumerates the key differences between electrolytic cells vs galvanic cells. However, both cells contain two half-cells for a net-redox reaction with reduction and oxidation. In both cells, oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction at the cathode. An electrolytic cell is a device designed to utilize electrical energy and facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Thus, electrical energy is converted to chemical energy via the process of electrolysis. The process involving the passage of electric current from an external source into a solution of electrolyte is called electrolysis. An electrolytic cell is suitable for the electrolysis of certain compounds such as water when subjected to electrolysis forms gaseous hydrogen and oxygen. The following electrolytic cell diagram shows the primary components of an electrolytic cell see figure 1. An electrolytic cell has an electrolytic tank made of a non-conducting material such as bakelite or glass.
Simultaneously, the chlorine atoms are attracted to the positively charged cathode. The half-reactions can be expressed as follows:. Most importantly, it must contain ions that are harder to oxidize or reduce than water.
Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis for the batteries that fuel modern society. But they are not the only kind of electrochemical cell. The reverse reaction in each case is non-spontaneous and requires electrical energy to occur. It is possible to construct a cell that does work on a chemical system by driving an electric current through the system.
An electrolytic cell can be defined as an electrochemical device that uses electrical energy to facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells that can be used for the electrolysis of certain compounds. For example, water can be subjected to electrolysis with the help of an electrolytic cell to form gaseous oxygen and gaseous hydrogen. This is done by using the flow of electrons into the reaction environment to overcome the activation energy barrier of the non-spontaneous redox reaction. The electrolyte provides the medium for the exchange of electrons between the cathode and the anode. Commonly used electrolytes in electrolytic cells include water containing dissolved ions and molten sodium chloride. Click here to learn more about the difference between Galvanic cells and electrolytic cells.
Electrolytic cell diagram
In , two scientists announced that they had achieved "cold fusion", the process of fusing together elements at essentially room temperature to achieve energy production. The hypothesis was that the fusion would produce more energy than was required to cause the process to occur. Their process involved the electrolysis of heavy water water molecules containing some deuterium instead of normal hydrogen on a palladium electrode. The experiments could not be reproduced and their scientific reputations were pretty well shot. However, in more recent years, both industry and government researchers are taking another look at this process. The device illustrated above is part of a government project, and NASA is completing some studies on the topic as well. Cold fusion may not be so "cold" after all.
Espn nhl hockey standings
Sacrificial protection is the process of protecting a metal at the expense of some other more active or electropositive metal coated on its surface. Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are called electrolytic cells. Voltaic cells use the energy given off in a spontaneous reaction to do electrical work. Where are electrolytic cells used? The substance with a lower standard reduction potential is preferentially oxidized at the anode. The process involving the passage of electric current from an external source into a solution of electrolyte is called electrolysis. Frequently Asked Questions Q1. Aluminium is obtained from bauxite using an electrolytic cell. Uses Of Benzene. The suffix - lysis comes from the Greek stem meaning to loosen or split up. Electrolytic Cells — convert electrical to chemical energy.
Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis for the batteries that fuel modern society. But they are not the only kind of electrochemical cell.
When this diaphragm is removed from the cell, the products of the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride react to form sodium hypo-chlorite, which is the first step in the preparation of hypochlorite bleaches, such as Chlorox. What are the uses of electrolytic cells? Share Share Share Call Us. Determine the oxidation number of the chromium in an unknown salt if electrolysis of a molten sample of this salt for 1. The deciding factor is a phenomenon known as overvoltage , which is the extra voltage that must be applied to a reaction to get it to occur at the rate at which it would occur in an ideal system. The substance with a lower standard reduction potential is preferentially oxidized at the anode. We can extend the general pattern outlined in this section to answer questions that might seem impossible at first glance. If you melt sodium chloride to obtain a liquid and pass an electric current through the molten salt, it decomposes. An idealized cell for the electrolysis of sodium chloride is shown in the figure below. Electrolytic cells can be used to produce oxygen gas and hydrogen gas from water by subjecting it to electrolysis. Click here to check your answer to Practice Problem

What words... super, a remarkable idea