Dsrna full form
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Double-stranded RNA dsRNA longer than 30 bp is a key activator of dsrna full form innate immune response against viral infections.
Understanding these roles is facilitated by mapping the genomic locations that express dsRNA in various tissues and organisms. In this review, we detail approaches to map ADAR editing sites and dsRNAs genome-wide, with particular focus on high-throughput sequencing methods and considerations for their successful application to the detection of editing sites and dsRNAs. Our goal in this review is to describe the unique properties dsRNA confers on a biological system and the techniques used for the genome-wide mapping of dsRNA i. In modern-day cells, nucleic acids play key and obvious roles, but they are also fundamental to self versus nonself discrimination Crowl et al. The diverse RNA editing and modifications found in all kingdoms of life, in recent years referred to as the Epitranscriptome Saletore et al. Perhaps reflecting an ancient and ongoing conflict between cells and selfish elements, in modern cells, dsRNA-mediated pathways play critical roles in immune defense in response to viral infection. Viruses have long been known to give rise to dsRNA Ehrenfeld and Hunt , which acts in the cytoplasm as a pathogen-associated molecular pattern PAMP , to trigger an immune response.
Dsrna full form
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Viruses with double-stranded RNA genomes form isometric particles or are capsidless. Here we report a double-stranded RNA virus, Colletotrichum camelliae filamentous virus 1 CcFV-1 isolated from a fungal pathogen, that forms filamentous particles. When inoculated, the naked CcFV-1 double-stranded RNAs are infectious and induce the accumulation of the filamentous particles in vivo. CcFV-1 is phylogenetically related to Aspergillus fumigatus tetramycovirus-1 and Beauveria bassiana polymycovirus-1, but differs in morphology and in the number of genomic components. CcFV-1 might be an intermediate virus related to truly capsidated viruses, or might represent a distinct encapsidating strategy. In terms of genome and particle architecture, our findings are a significant addition to the knowledge of the virosphere diversity. Viruses infect all cellular organisms including protozoa, bacteria, archaea, invertebrates, vertebrates, algae, plants, and fungi 1. Their morphotypical peculiarities have been impacted by the environment and the specific nature of the host, which is particularly noticeable in archaeal viruses 2 , 3 , 4. Viruses that infect plants and fungi display moderate morphotypical diversity, forming bacilliform, icosahedral, or filamentous viral particles virions , which are closely related with their taxon, evolution, and host 1 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8. DsRNA viruses are a diverse group that infect a wide range of hosts, from bacteria to eukaryotes including fungi, protozoa, plants, and animals 1. Most dsRNA viruses present isometric particles, including members of the families Totiviridae non-segmented genome, 4.
Interview Click to see an interview with subject dsrna full form editor Mark Estelle. We first discuss the dsRNA sensors in the vertebrate innate immune system, with the focus on their signalling pathways, mechanisms and RNA specificity.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Double-stranded RNA dsRNA is associated with most viral infections — it either constitutes the viral genome in the case of dsRNA viruses or is generated in host cells during viral replication. Hence, nearly all organisms have the capability of recognizing dsRNA and mounting a response, the primary aim of which is to mitigate the potential infection. In vertebrates, a set of innate immune receptors for dsRNA induce a multitude of cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic immune responses upon dsRNA recognition. Notably, recent studies showed that vertebrate cells can accumulate self-derived dsRNAs or dsRNA-like species upon dysregulation of several cellular processes, activating the very same immune pathways as in infected cells.
Posted on October 31st, by Lawrence Tabak, D. In rare cases, a virus can infect the brain. For this reason, the brain, more than other parts of the body, relies heavily on immune responses that can control viral infections immediately. Now some intriguing findings from an NIH-funded team reported in Science Immunology help to explain how the brain is protected against infections. They also point to promising targets for developing treatments that might turn inflammatory immune responses in the brain up or down, as desired, to treat these and other serious conditions. RNA molecules are readouts of genetic information in DNA that carry instructions for building the proteins that carry out various cell functions. In contrast, lengthy dsRNAs are a hallmark of viruses. Their lab studies in cells and tissues show that these dsRNAs in neurons can trigger an inflammatory immune response just as they do in viruses. By manipulating neurons in a way that cut back on the number of dsRNAs, they found they could lower the innate immune response. However, cells with fewer dsRNAs also showed greater susceptibility to infection with Zika viruses and herpes simplex virus, which can produce a form of viral encephalitis.
Dsrna full form
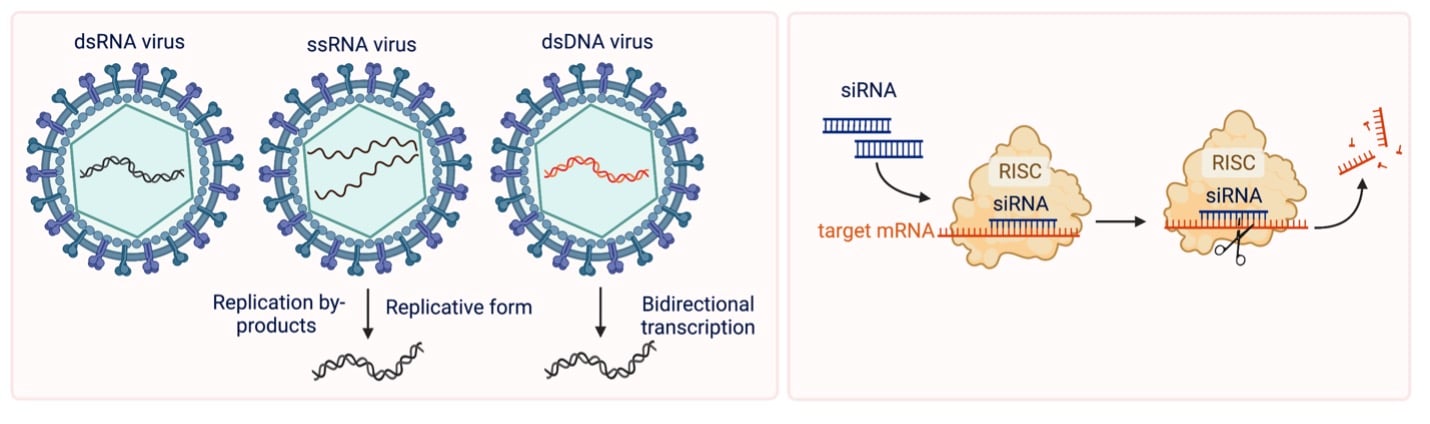
Transcription, translation, and prone to degradation — those are the words that describe RNA! Double stranded? RNA performs almost all of its biological functions in our cells in the single strand form, but double stranded RNA and RNA:DNA hybrid molecules both exist and have a diverse range of functions within mammalian cells. Viral genomes come in all sorts of shapes and sizes. Still others use dsDNA to store their genetic information. In an uninfected cell, dsRNA rarely circulates, but upon viral infection, this nucleic acid can build up. The foreign dsRNA activates the innate immune response machinery of the host.
Mid century handles
In addition to modifying host transcripts, m 6 A also modifies viral RNAs. The most straightforward is to choose candidate edited regions for editing validation by another method, typically cDNA amplification and Sanger sequencing Li et al. This work was supported by grants from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities no. Cell Rep 9 : — Nelson AM et al. Xie, J. CcFV-1 can impair host cellular homeostasis, confer hypovirulence, and impact host morphology, including pigment production and distribution, growth rate and hyphal ring generation. The nucleic acids were precipitated with ethanol, dissolved in DEPC-treated water and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Novoa, R. The third large group of viruses comprises the negative-strand RNA viruses. Georgel, E. Cell 55 : —
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
L1 retrotransposition is suppressed by endogenously encoded small interfering RNAs in human cultured cells. Cossaviricota Mouviricetes Polivirales Bidnaviridae. Blakqori, V. Streitenfeld, H. Arana, J. Genes Dev 25 , — Evstafieva, Y. Vartapetian, and V. Genetic and phenotypic spectrum associated with IFIH1 gain-of-function. Hence, nearly all organisms have the capability of recognizing dsRNA and mounting a response, the primary aim of which is to mitigate the potential infection. Wikimedia Commons Wikispecies.

Speaking frankly, you are absolutely right.
Many thanks.