Draw position time graph for uniform motion
Byju's Answer.
Our study of 1-dimensional kinematics has been concerned with the multiple means by which the motion of objects can be represented. Such means include the use of words, the use of diagrams, the use of numbers, the use of equations, and the use of graphs. Lesson 3 focuses on the use of position vs. As we will learn, the specific features of the motion of objects are demonstrated by the shape and the slope of the lines on a position vs. The first part of this lesson involves a study of the relationship between the shape of a p-t graph and the motion of the object. If the position-time data for such a car were graphed, then the resulting graph would look like the graph at the right. Note that a motion described as a constant, positive velocity results in a line of constant and positive slope when plotted as a position-time graph.
Draw position time graph for uniform motion
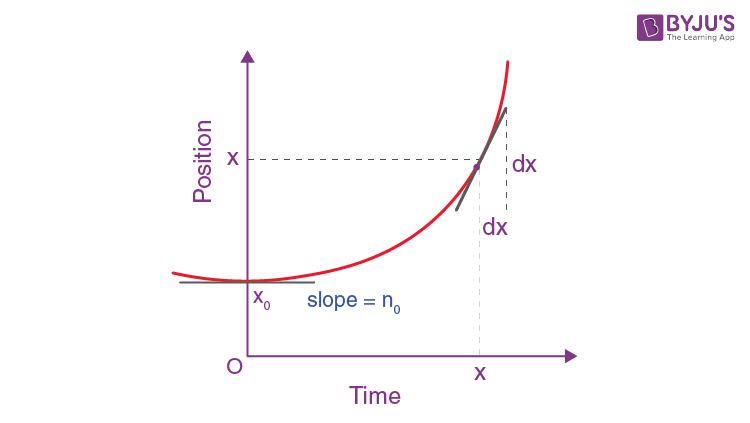
One of the most elementary forms of graphs in kinematics is the Position-time graph , which helps us to define the motion of a body. In these graphs, the position of the object is represented by the vertical axis, the time elapsed is represented by the horizontal axis, and the dependent variable, that is position, depends on the independent variable, that is time. In this way, the graph expresses to us where the particle can be found after some time. These graphs help us visualise the path of objects. By studying a position-time graph for an object, we can analyse the path and position of an object precisely. The graph on which the instantaneous position x of a particle is plotted on the y-axis and the time t on the x-axis is known as the Position-Time graph. Since this article is an explanation of the position-time graph, before digging deep into the details of the topic let us first understand how to draw these graphs. In the case of the Kinematic equation for uniformly accelerated motion , position is a dependent variable and time will be our fundamental independent variable. Also, the other dependent variables will be displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Therefore, in uniform rectilinear motion the Position-time graph for an object is a straight line inclined to the time axis. For uniformly accelerated motion along a straight line the Position Time relation will be given as,. Here, x depends on t 2 which shows that it is a quadratic equation of function t, therefore, for uniform accelerated motion the position-time graph is a parabola.
Draw the position-time graph for an object in uniform motion. To find displacement ref above diagram. Steps to draw a position-time graph for uniform motion.
Position time Graph For Uniform Motion. Let us find out displacement for a body moving in uniform motion at a uniform velocity with zero acceleration. To find displacement ref above diagram. Steps to draw a position-time graph for uniform motion. Recommended Read: What is uniform motion?
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Displacement, velocity, and time. See what we can learn from graphs that relate position and time. How are position vs. Many people feel about graphs the same way they do about going to the dentist: a vague sense of anxiety and a strong desire for the experience to be over with as quickly as possible. But position graphs can be beautiful, and they are an efficient way of visually representing a vast amount of information about the motion of an object in a conveniently small space. What does the vertical axis represent on a position graph? The vertical axis represents the position of the object.
Draw position time graph for uniform motion
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user? Log in.
Aubreyluvsss porn
Be complete in your description. Its initial velocity is u and after time t its velocity is v. Focal Length Formula. The graph on the right also depicts an object with negative velocity since there is a negative slope. In this way, the graph expresses to us where the particle can be found after some time. The graph on which the instantaneous position x of a particle is plotted on the y-axis and the time t on the x-axis is known as the Position-Time graph. The object begins with a high velocity the slope is initially large and finishes with a small velocity since the slope becomes smaller. These graphs help us visualise the path of objects. As the object is in uniform motion this implies that the object covers equal distance in equal interval of time. Draw the position-time graph of a stationary object. So this object is moving in the negative direction and slowing down.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos.
A race car accelerates on a straight road from rest to a speed of The velocity-time graph of a body moving along a straight line is given below find: a Average velocity in whole time of motion b Average speed in whole time of motion c Draw acceleration vs time graph. Post My Comment. In your description, be sure to include such information as the direction of the velocity vector i. As the slope goes, so goes the velocity. Position — Y-Axis. The principle of slope is an incredibly useful principle for extracting relevant information about the motion of objects as described by their position vs. The object represented by the graph on the right is traveling faster than the object represented by the graph on the left. A cyclist moving on a circular track of radius m completes one rev X-T Graph. The slope of the position time graph represents the velocity of an object. Such means include the use of words, the use of diagrams, the use of numbers, the use of equations, and the use of graphs. The shapes of the position versus time graphs for these two basic types of motion - constant velocity motion and accelerated motion i.

0 thoughts on “Draw position time graph for uniform motion”