Cuda cores meaning
CUDA is a software layer that gives direct access to the GPU's virtual instruction set and parallel computational elements for the execution of compute kernels.
But as datasets increase in volume, complexity and cross-relationships, the demand for processing power also surges exponentially. It is, therefore, even more inherently dependent on ingesting massive volumes of data to feed the model. Traditional CPUs cannot handle such massive data workloads, nor can they deliver the computational power for ML model training. As a consequence of not possessing the requisite processing power, often the entire system lags and grinds to a screeching halt. This article will give a complete walkthrough of the impact of GPU accelerated analytics platforms on ML. We will also gather insights into the differences between CUDA and Tensor cores and determine which one is the best fit for ML undertakings.
Cuda cores meaning
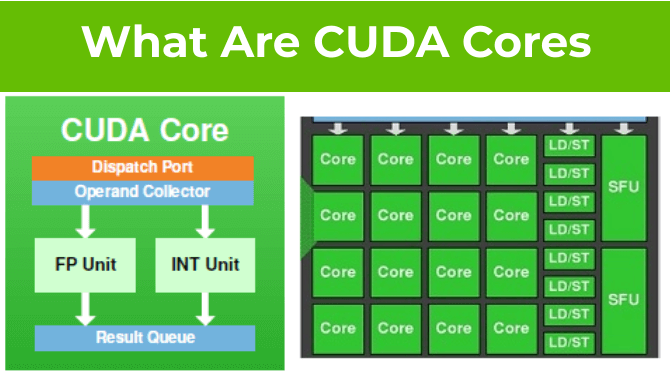
But what are they? How are they different from regular CPU cores? First introduced in , they have since become an important part of high-performance computing. In this blog, we will explain what CUDA cores are and how they differ from other types of cores. We will also discuss the advantages of using CUDA cores and ways to employ them for accelerating performance. In short, these are special types of cores that are designed to speed up certain types of calculations, particularly those that are needed for graphics processing. GPUs with lots of CUDA cores can perform certain types of complex calculations much faster than those with fewer cores. These cores are used to process and render images, video, and other visual information for both display devices like monitors and TVs, and for computer vision applications. One of the most important questions that any computer hardware manufacturer likes to answer is how many cores are in their device. CUDA cores are specialized cores designed for parallel computing. They are different from other cores such as tensor cores, CPU cores, etc. While CUDA cores are more specialized than other types of cores, they offer a significant performance boost for certain types of applications such as time-intensive workloads, gaming, and deep learning. If your application can benefit from parallel computing, then CUDA cores can offer a major performance advantage. CUDA cores are powerful components of your GPU which are capable of handling multiple tasks simultaneously and can deliver significant compute performance for computer graphics and general-purpose computing.
GeForce 3 4 Ti FX 6 7. Tom's Hardware. Technical specifications Compute capability version 1.
Trusted Reviews is supported by its audience. If you purchase through links on our site, we may earn a commission. Learn more. On the lookout for a new GPU and not totally sure what you should be looking for? It will work with most operating systems.
She's a computer science graduate and has been writing about design, creativity and technology. It may or may not be necessary in a deep learning framework. On the other side, Tensorflow appears to demand it. A system with more than one CPU can do parallel processing. It is a process when a task is handled in parallel, it means that at least two microprocessors are used simultaneously. Parallel processing is possible on systems with several CPUs, including the multi-core processors that are frequently used in modern computers.
Cuda cores meaning
Graphics Processing Units GPUs can either come integrated on your processor, or on a dedicated graphics card. Check out our article on the differences between integrated and dedicated graphics. GPUs process all screen-destined content and graphics that computers and gaming consoles produce. Many computer users are familiar with CPUs , as they are often advertised prominently with new computers. Most modern CPUs are dual- or quad-core, meaning they have two or four core components capable of processing data. Another reason for the discrepancy in how many cores are found in GPUs is that graphics cards tend to be about four to eight times larger in physical size than CPUs, allowing more real estate for chips.
Cpi quizlet
By , GPUs had evolved into highly parallel multi-core systems allowing efficient manipulation of large blocks of data. Branch prediction Memory dependence prediction. June 23, Your email address will not be published. What is the Apple M3 chip? The AI feature explained. The major benefit of these cores is that they can offer a significant boost to performance when it comes to certain types of parallel processing tasks such as machine learning and artificial intelligence. Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published. In other projects. Nolan Foster. Connect with us. Pascal without Tensor core is only shown for speed comparison as is Volta V with non-FP16 datatypes. Contact Sales. CUDA was created by Nvidia. Read our Privacy Policy.
You'll hear people rave about these mysterious cores, but you still have no idea how they improve a GPU.
GeForce 2 4 MX. Retrieved 22 March This article will give a complete walkthrough of the impact of GPU accelerated analytics platforms on ML. CUDA is a software layer that gives direct access to the GPU's virtual instruction set and parallel computational elements for the execution of compute kernels. Max number of new instructions issued each cycle by a single scheduler [97]. He is well versed in the dynamic trends of cloud computing and cybersecurity. The more cores you have, the faster your system can process information. In short, these are special types of cores that are designed to speed up certain types of calculations, particularly those that are needed for graphics processing. December 8, GeForce 3 4 Ti FX 6 7.

0 thoughts on “Cuda cores meaning”