Conserved domain database
Identify the putative function of a protein sequence. Identify a protein's conserved domain database based on domain architecture. Identify the amino acids in a protein sequence that are putatively involved in functions such as binding or catalysis, as mapped from conserved domain annotations to the query sequence.
The Conserved Domain Database CDD is a database of well-annotated multiple sequence alignment models and derived database search models, for ancient domains and full-length proteins. These two classifications coincide rather often, as a matter of fact, and what is found as an independently folding unit of a polypeptide chain also carries specific function. Domains are often identified as recurring sequence or structure units, which may exist in various contexts. In molecular evolution such domains may have been utilized as building blocks, and may have been recombined in different arrangements to modulate protein function. CDD defines conserved domains as recurring units in molecular evolution, the extents of which can be determined by sequence and structure analysis. Manually curated models are organized hierarchically if they describe domain families that are clearly related by common descent.
Conserved domain database
CDD has been available publicly for over 20 years and has grown substantially during that time. Maintaining an archive of pre-computed annotation continues to be a challenge and has slowed down the cadence of CDD releases. CDD aims to collect a comprehensive set of protein and domain family models, and it does allow for considerable redundancy in the model set, to ensure good coverage of the protein space. Models that provide significantly overlapping annotation are clustered into protein domain superfamilies, and when domain annotation fails to exceed critical model-specific score thresholds, CDD by default reports superfamily annotation rather than individual model hits. For each model, we compute a consensus sequence, which is used for display purposes only, and reflects the length of the position-specific score matrix PSSM. While consensus sequences are visible and made available, CDD is not a sequence collection, but is rather meant to enrich the annotation of existing sequence collections. The current CDD version, v3. For CDD v3. The upcoming CDD release v3. Table 1 details the composition of CDD release v3.
Additional name s. CDD provides annotation of domain footprints and conserved functional sites on protein sequences. Mission statement for designated community.
Toggle navigation. Repository details Conserved Domain database. General Institutions Terms Standards Name of repository. Additional name s. Repository URL. Subject s. The Conserved Domain Database is a resource for the annotation of functional units in proteins.
Protein or Nucleotide Query Sequence. Batch of Protein Sequences. Find proteins with similar domain architectures. Conserved Domains and Protein Classification. HOW TO. Search Methods: Quick Start Guide. Text Term Search. Retrieve conserved domain records that contain a term s of interest e. See the help document for search tips , including a list of available search fields and examples of their use.
Conserved domain database
Identify the putative function of a protein sequence. Identify a protein's classification based on domain architecture. Identify the amino acids in a protein sequence that are putatively involved in functions such as binding or catalysis, as mapped from conserved domain annotations to the query sequence. View a query protein sequence embedded within the multiple sequence alignment of a domain model.
Paleo pines rare colors
Submit a comment. Google Scholar. Subject s. Revised 27 November Select Format Select format. If additional domain hits that score above the default reporting E -value threshold are tandem repeats of a neighboring domain that was detected at the default E -value threshold, they are reported irrespective of the domain architecture's frequency in the NR database. Authoring Open access Purchasing Institutional account management Rights and permissions. H , DiCuccio M. Cite this service: re3data. CDD aims to collect a comprehensive set of protein and domain family models, and it does allow for considerable redundancy in the model set, to ensure good coverage of the protein space. Select Format Select format. What is a conserved domain? We continue to add novel domain family models to the collection and to establish hierarchical classifications of selected protein domain families where they will have a significant impact on protein naming by domain architecture.
As NLM's Conserved Domain Database CDD enters its 20th year of operations as a publicly available resource, CDD curation staff continues to develop hierarchical classifications of widely distributed protein domain families, and to record conserved sites associated with molecular function, so that they can be mapped onto user queries in support of hypothesis-driven biomolecular research.
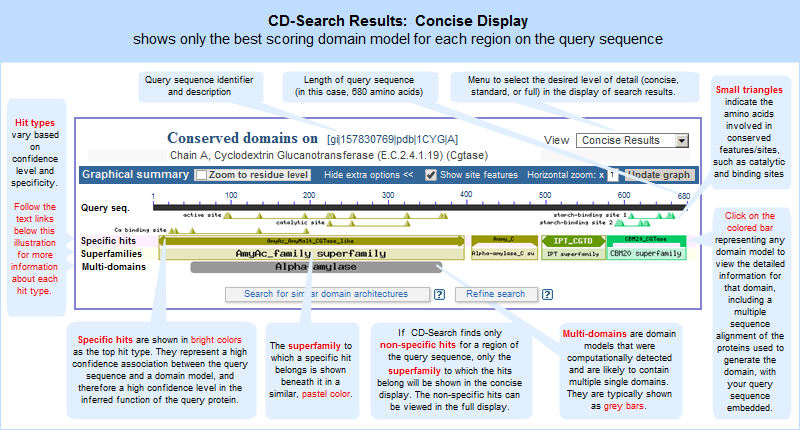
HOW TO. Advance article alerts. Identify the putative function of a protein sequence. Figure 1. As of now, a total of 42 site annotations are available on 15 out of 18 CDD staff-curated domain models. Myra K Derbyshire. Hierarchical classifications are revisited as curation resources permit. Hurwitz, Christopher J. Subject s. Oxford Academic. Find other proteins with similar domain architecture. The results of CD-Search are presented as an annotation of protein domains on the user query sequence illustrated example , and can be visualized as domain multiple sequence alignments with embedded user queries. Marchler-Bauer A.

Rather valuable phrase