Chitinase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Chitinases have the ability of chitin digestion that constitutes a main compound of the cell wall in many of the phytopathogens such as fungi. In the following investigation, a novel chitinase with antifungal activity was characterized from a native Serratia marcescens B4A. Partially purified enzyme had an apparent molecular mass of 54 kDa. Moreover, the Km and Vmax values for chitin were 8. Additionally, the effect of some cations and chemical compounds were found to stimulate the chitinase activity. In addition, Iodoacetamide and Idoacetic acid did not inhibit enzyme activity, indicating that cysteine residues are not part of the catalytic site of chitinase.
Chitinase
Molecular and Cellular Pediatrics volume 2 , Article number: 3 Cite this article. Metrics details. Chitin, after cellulose, the second most abundant biopolymer on earth, is a key component of insects, fungi, and house-dust mites. Lower life forms are endowed with chitinases to defend themselves against chitin-bearing pathogens. Unexpectedly, humans were also found to express chitinases as well as chitinase-like proteins that modulate immune responses. Particularly, increased levels of the chitinase-like protein YKL have been associated with severe asthma, cystic fibrosis, and other inflammatory disease conditions. Here, we summarize and discuss the potential role of chitin, chitinases, and chitinase-like proteins in pediatric lung diseases. The role of chitin and chitinases has been firmly established in the field of plant and microbial immunity by demonstrating that host-derived chitinases cleave chitin to protect against invading chitin-bearing pathogens, such as fungi. Although mammals lack endogenous chitin or chitin synthases, chitinases and chitinase-like proteins are endogenously expressed in their lung and other organs. Particularly, chitinase-like proteins have been described as dysregulated in a variety of diseases characterized by chronic inflammation and tissue remodeling, yet their potential role for humans has just recently begun to evolve [ 1 , 2 ]. Chitin is a major component of a variety of allergy-triggering environmental components, including house-dust mites or fungal spores, and fungal asthma is increasingly appreciated as an under-diagnosed disease entity [ 3 ]. Thus, an understanding of the complex immunological and pathophysiological implications of chitin-chitinase interactions in the human body is of high relevance for identifying new biomarkers and therapeutic targets for fungal diseases and other conditions, where chitin-coated microbial derivatives play a critical role.
Lu et al.
Ayokunmi Oyeleye , Yahaya M. Normi; Chitinase: diversity, limitations, and trends in engineering for suitable applications. Chitinases catalyze the degradation of chitin, a ubiquitous polymer generated from the cell walls of fungi, shells of crustaceans, and cuticles of insects. They are gaining increasing attention in medicine, agriculture, food and drug industries, and environmental management. Their roles in the degradation of chitin for the production of industrially useful products and in the control of fungal pathogens and insect pests render them attractive for such purposes.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Food allergies originate from adverse immune reactions to some food components. Ingestion of food allergens can cause effects of varying severity, from mild itching to severe anaphylaxis reactions. Currently there are no clues to predict the allergenic potency of a molecule, nor are cures for food allergies available. Cutting-edge research on allergens is aimed at increasing information on their diffusion and understanding structure-allergenicity relationships. In this context, purified recombinant allergens are valuable tools for advances in the diagnostic and immunotherapeutic fields. Chitinases are a group of allergens often found in plant fruits, but also identified in edible insects.
Chitinase
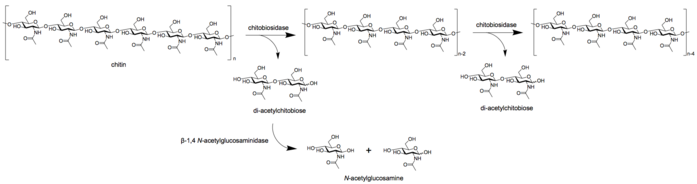
Chitinases are widely distributed enzymes and are present in a wide range of organisms including insects, plants, bacteria, fungi, and mammals. These enzymes play key roles in immunity, nutrition, pathogenicity, and arthropod molting. Human chitinases are reported to play a protective role against chitin-containing pathogens through their capability to degrade chitin present in the cell wall of pathogens. Now, human chitinases are gaining attention as the key players in innate immune response. Although the exact mechanism of their role in immune response is not known, studies in recent years begin to relate chitin recognition and degradation with the activation of signaling pathways involved in inflammation. The roles of both CHIT1 and AMCase in the development of various diseases have been revealed and several classes of inhibitors have been developed. However, a clear understanding could not be established due to complexities in the design of the right experiment for studying the role of human chitinase in various diseases. We will then review the progress in understanding the role of human chitinases in the development of various diseases. Publication types Review. Substances Chitin Chitinases.
Oslo euronext live
Allosamidin inhibits the fragmentation of Acremonium chrysogenum but does not influence the cephalosporin-C production of the fungus. Gaber et al. The Plant Journal. Seed Ecology Chapter However, family 19 chitinases are not known to be affected by any of these inhibitors. Chitinibacter sp. Solid-State Fermentation SSF for Chitinase Production Nutrient-rich waste materials, such as bagasse, paper pulp, and bran, can be used as substrates in SSF, for producing different metabolites, including chitinases. Role of Chitinases as a waste management to control global crisis. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the regulation of ScCts1p S. Unearthing the role of septins in viral infections. Respir Med 12 —, doi Bacterial chitinase with phytopathogen control capacity from suppressive soil revealed by functional metagenomics. Statistical optimization of chitinase production by Box—Behnken design in submerged fermentation using Bacillus cereus GS Clin Exp Allergy 42 4 —, doi
Non-enzymatic chitinase-3 like-protein-1 CHI3L1 belongs to glycoside hydrolase family It binds to chitin, heparin, and hyaluronic acid, and is regulated by extracellular matrix changes, cytokines, growth factors, drugs, and stress.
Chromobacterium violaceum. Fermentation Period For the production of chitinase, the fermentation period varies with the organism, substrate used, and other process parameters. Cell Factories. TIM triosephosphate isomerase. Allosaminidin is the inhibitor of insect chitinases. Beyond asthma and CF, circulating YKL has been further associated with decline of lung function in the general population and has been proposed as a biomarker of susceptibility to the long-term effects of cigarette smoking [ 62 ]. In general, the optimum pH and temperature of fungal chitinases range from 4. Keywords: chitinolytic enzymes, microbial chitinases, chitooligosaccharides, fermentation, biocontrol. Recently, the wide use of molecular methods in the study of microbes and their complex roles in the environment have helped to breakdown some microbial processes controlling chitin degradation [ 45 ]. Further studies showed that the allergen ovalbumin increased YKL expression in tracheal epithelial cells [ 69 ] and demonstrated that YKL increased mucin5AC production in human bronchial epithelial cells [ 70 ]. Biocontrol Agent Several pathogens, such as Fusarium sp. For instance, processive Sm ChiB might be useful in the hydrolysis of chitin for marine waste management, Sp ChiD might be more suitable for the synthesis of long chain COS because of their transglycosylating property [ 88 ], and Chi42 from T.

I am sorry, it not absolutely approaches me. Who else, what can prompt?
I join told all above. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
What words... super, excellent idea