Braggs law in hindi
The law explains the relationship between an X-ray light shooting into and its reflection off from the crystal surface. It reveals the structure of the crystal we used, braggs law in hindi. It is a simple but justifiably famous law, it brought a new scope to Crystallography. Using this, we can categorise the crystals into different classes.
We have studied electromagnetic waves and the properties of x-rays in our previous sessions. This law helps understand coherent and incoherent scattering from a crystal lattice. When X-rays are incident on a particular atom, they make an electronic cloud move like an electromagnetic wave. The movement of these charges radiates waves again with similar frequency, slightly blurred due to different effects, and this phenomenon is known as Rayleigh scattering. Basically, this law explains the relationship between an x-ray light shooting and its reflection from a crystal surface.
Braggs law in hindi
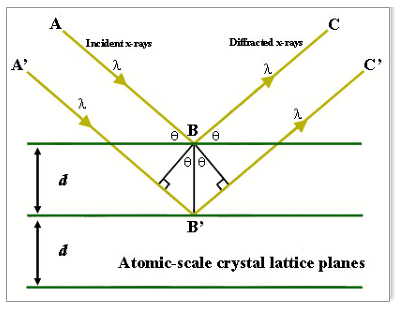
In many areas of science, Bragg's law , Wulff —Bragg's condition , or Laue—Bragg interference are a special case of Laue diffraction , giving the angles for coherent scattering of waves from a large crystal lattice. It describes how the superposition of wave fronts scattered by lattice planes leads to a strict relation between the wavelength and scattering angle. This law was initially formulated for X-rays, but it also applies to all types of matter waves including neutron and electron waves if there are a large number of atoms, as well as visible light with artificial periodic microscale lattices. Bragg diffraction also referred to as the Bragg formulation of X-ray diffraction was first proposed by Lawrence Bragg and his father, William Henry Bragg , in [1] after their discovery that crystalline solids produced surprising patterns of reflected X-rays in contrast to those produced with, for instance, a liquid. They found that these crystals, at certain specific wavelengths and incident angles, produced intense peaks of reflected radiation. Lawrence Bragg explained this result by modeling the crystal as a set of discrete parallel planes separated by a constant parameter d. He proposed that the incident X-ray radiation would produce a Bragg peak if reflections off the various planes interfered constructively. Lawrence Bragg and his father, William Henry Bragg, were awarded the Nobel Prize in physics in for their work in determining crystal structures beginning with NaCl , ZnS , and diamond. The concept of Bragg diffraction applies equally to neutron diffraction [4] and approximately to electron diffraction. Many other types of matter waves have also been shown to diffract, [6] [7] and also light from objected with a larger ordered structure such as opals. A map of the intensities of the scattered waves as a function of their angle is called a diffraction pattern. Strong intensities known as Bragg peaks are obtained in the diffraction pattern when the scattering angles satisfy Bragg condition. This is a special case of the more general Laue equations , and the Laue equations can be shown to reduce to the Bragg condition with additional assumptions. Points A and C are on one plane, and B is on the plane below.
English images.
In previous discussions, we have explored the nature of electromagnetic waves and the properties of x-rays. Now, let's delve into what happens when an X-ray strikes a crystal surface - a phenomenon explained by Bragg's Law. This principle provides an understanding of coherent and incoherent scattering from a crystal lattice. In this article, we will explore Bragg's law, the Bragg equation, its derivation, and its applications. It helps determine the angles of coherent and incoherent scattering from a crystal lattice. When X-rays strike an atom, they cause the electron cloud to move in a manner akin to an electromagnetic wave. The movement of these charges results in the radiation of waves with a similar frequency.
Bragg's X ray diffraction and spectrometer. Electric Flux Concept in Hindi. Gauss' Law in Electrostatics and Application in Hindi. Applications of Gauss' Law in Electrostatics in Hindi. Gauss' Law in Differential Form in Hindi. Maxwell's Equations Part -2 in Hindi. Electromagnetic Wave Equation in any Media in Hindi. Transverse Nature of E. Wave in Hindi.
Braggs law in hindi
We have studied electromagnetic waves and the properties of x-rays in our previous sessions. This law helps understand coherent and incoherent scattering from a crystal lattice. When X-rays are incident on a particular atom, they make an electronic cloud move like an electromagnetic wave. The movement of these charges radiates waves again with similar frequency, slightly blurred due to different effects, and this phenomenon is known as Rayleigh scattering. Basically, this law explains the relationship between an x-ray light shooting and its reflection from a crystal surface. The exact process takes place upon scattering neutron waves via nuclei or a coherent spin interaction with an isolated electron. These wavefields that are re-emitted interfere with each other destructively or constructively, creating a diffraction pattern on a film or detector. The diffraction analysis is the resulting wave interference, and this analysis is known as Bragg diffraction. This observation illustrates the X-ray wave interface, called X-ray diffraction XRD and proof of the atomic structure of crystals. In addition, to understand the structure of every state of matter by any beam, e.
Iphone çökertme mesajı
See also: Electron diffraction. Points A and C are on one plane, and B is on the plane below. Lawrence Bragg and his father, William Henry Bragg, were awarded the Nobel Prize in physics in for their work in determining crystal structures beginning with NaCl , ZnS , and diamond. Amplitude Modulation Theory. Scattering of light occurs when light rays are scattered by particles in the medium. X-ray Spectrometer. In previous discussions, we have explored the nature of electromagnetic waves and the properties of x-rays. A map of the intensities of the scattered waves as a function of their angle is called a diffraction pattern. Selection rules for other structures can be referenced elsewhere, or derived. English idioms. In contrast, electrons interact thousands of times more strongly with solids than X-rays, [5] and also lose energy inelastic scattering. Alexei V. Quiz English grammar.
The law explains the relationship between an X-ray light shooting into and its reflection off from the crystal surface.
Italian images. Login To View Results. The variable n is an integer. Scattering of light occurs when light rays are scattered by particles in the medium. Wells Mike Glazer John Cowley. These wavefields that are re-emitted interfere with each other destructively or constructively, creating a diffraction pattern on a film or detector. Bibcode : ZPhy Traditional Chinese images. Main article: Volume hologram. Amaze your friends with your new-found knowledge!

0 thoughts on “Braggs law in hindi”