Bbc bitesize national 5 physics
The National 5 Physics exam is made up of two question papers. Paper 1 is a multiple choice paper.
The National 5 Physics exam is made up of two question papers. Paper 1 is a multiple choice paper. Paper 2 is made up of questions with several parts that need written answers. Vectors and scalars. Scalars have a size, while vectors have both size and direction.
Bbc bitesize national 5 physics
Use these links to download the SQA National 5 relationship sheet and data sheet. These papers and solutions are reproduced to support SQA qualifications on a non-commercial basis according to SQA conditions of use. The sections below contain links to revision notes, PowerPoint slides and extra questions to test your readiness for assessments in each of the units. Or, if you have a Glow username and password, download a copy of Microsoft Office from the tile on your home page. Alternatively, why not download the free LibreOffice office suite? You can also create your own files and save them so that you can open them in school with Microsoft Office. Some of the pdf files have been created by converting PowerPoint files. In places where the original slide is animated, you will need to read several pages in a row to see the full slide contents. Check this blog post to find out how you can get free physics revision software for home use only. Vector Scale Diagrams from mr mackenzie on Vimeo. Try these relative velocity problems. Click on the picture below to try this simulation.
Radiation can have destructive effects but can also be used in medicine, industry and electricity generation. AC and DC Electricity. Set the variables and click start.
.
Electrical charge carriers. Electrical current is electrical charge transferred in a particular time. Current can be a. Potential differences voltage. The potential difference or voltage of a supply is a measure of the energy given to the charge carriers in a circuit. Practical electrical and electronic circuits.
Bbc bitesize national 5 physics
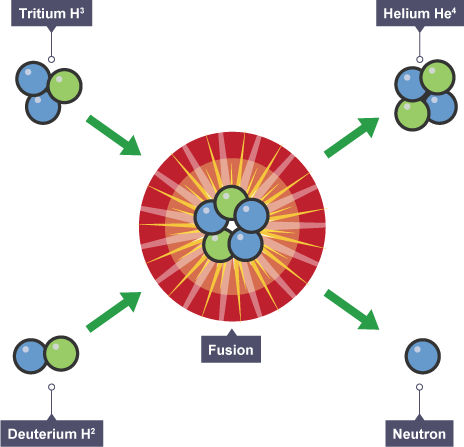
If the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons then the atom is uncharged and is electrically neutral. Ionisation close ionisation Process by which electrons can be added or removed from an atom to create an ion. An atom's charge can only change through gaining or losing electrons. Protons cannot be added or removed because they are bound up with neutrons in the nucleus. Electrons can be lost because an ionising radiation something that you will study later in this chapter comes close to or collides with the atom and forces the electron away from the atom. If the atom is hit by an ionising radiation close radiation Energy carried by particles from a radioactive substance, or spreading out from a source. In this guide. The atom Ionisation Types of radiation Sources of radiation How radiation can be detected Other ways of detecting radiation Measuring half-life Dosimetry Equivalent dose Dose limits Safety and radioactive sources Nuclear reactions Nuclear power stations Fusion reactor.
Bill thesaurus
I might actually have a chance for an A in Physics! Energy The law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed - it can only be transferred from one type to another. Projectiles and satellites move in curved paths due to the effects of gravitational force. Specific heat capacity. Many thanks Amandeep Reply. The Physics Classroom. Graphs of motion Click on the picture below to try this simulation. Notice how the presenter converts the current from mA to A before doing the calculation in his example. A geostationary satellite is not actually stationary. Paper 1 is a multiple choice paper. Velocity-time graphs Velocity-time graphs are used to describe the motion of objects which are moving in a straight line. Measurement and analysis of current and voltage in simple circuits allows us to formulate rules and predict unknown values.
The National 5 Physics exam is made up of two question papers.
Okay thanks anyway! It can be calculated by dividing the change in velocity by the total time. Different materials have different latent heats. The vehicle slows down as its kinetic energy is lost. By considering motion in horizontal and vertical directions, we can predict their path. AC and DC Electricity. Refraction of light takes place in many places, including lenses and prisms. Physics Central. Acceleration Acceleration is the change in speed or velocity of an object over a certain time. Power is a measure of the rate of energy transfer and relates to the current and voltage for an electrical circuit.

As the expert, I can assist. I was specially registered to participate in discussion.
Be assured.