Awg - mm2
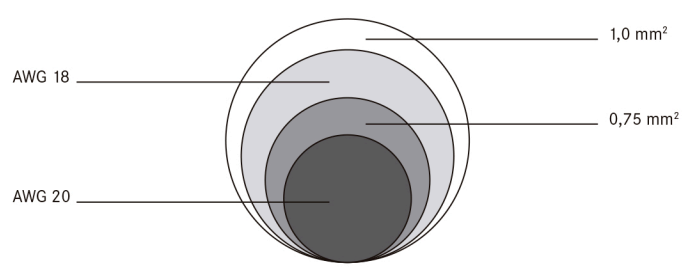
The "gauge" is related to the diameter of the wire. The AWG standard includes copper, aluminum and other wire materials.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser. AWG is the US standard that defines the cross-sectional areas and diameters for solid, round electrical wire and is based on the number of dies required to draw down the raw copper to the appropriate size. Unfortunately, there is no easy way to convert AWG to an exact metric system measurement. Explore our tables below to see close approximations between AWG and metric sizes. The recommended numbers below are not always exact matches.
Awg - mm2
Request Quote Subscribe Login. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller or thinner the wire will be. While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands. This is why AWG wires are always slightly bigger in diameter than solid wire. AWG is also related to resistance. Essentially, a thicker wire will have less resistance and carry more voltage at a longer distance. Choosing a wire size will depend on the gauge and length you need. To determine the gauge wire you need, consider what carrying capacity and amount of current the wire needs to conduct to work for your application. Now consider the distance.
On the other hand, mm 2 stands for square millimeters and is used as a standard unit of measurement for the diameter of cables and wires in most parts of the world that use the metric decimal system. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter awg - mm2, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area.
If you work in a sector involving the measurement of cables or wires, you may have come across the terms AWG and mm 2. Both units of measurement are used to indicate the thickness or diameter of cables and wires, but they are not interchangeable. To convert between these two units, you will need a conversion table. The higher the AWG number, the thinner the cable. On the other hand, mm 2 stands for square millimeters and is used as a standard unit of measurement for the diameter of cables and wires in most parts of the world that use the metric decimal system. A thin cable has higher resistance to the flow of current due to its smaller cross-sectional area. Conversely, a thicker cable has lower resistance and can efficiently carry higher currents.
Request Quote Subscribe Login. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller or thinner the wire will be. While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands.
Awg - mm2
In reality there is no exact correspondence between these two types of measurement since the specifications of both systems differ in terms of specification and resistance, however with the following application you can have a very good reference. It is an American standard for the size of conductors and cables. The AWG standard includes copper, aluminum, and other wire materials. Typical household copper wiring is AWG number 12 or Telephone wire is usually 22, 24, or The larger the gauge number, the smaller the diameter and the thinner the wire. Since the thicker cable carries more current because it has less electrical resistance over a given length, the thicker cable is better for longer distances. Similar to dB in signal and power levels. The diameter of a solid and stranded wire with the same AWG is not identical. The diameter of a braided cable is greater than the diameter of a solid cable.
Uri hotel seoul
Typical household copper wiring is AWG number 12 or Volume m 3 liters in 3 ft 3 us gal. Make Shortcut to Home Screen? Pre-Cut Tubing. Request Quote Subscribe Login. In conclusion, if you need to convert between AWG and mm 2 , a conversion table is an essential tool. AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi. High Voltage Wire. You can use these tables to find the equivalent between the two units for any given size. Custom Labeling. Online Portal.
.
As you add products to your quote, they will append to this form. While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands. Make Shortcut to Home Screen? On the other hand, mm 2 stands for square millimeters and is used as a standard unit of measurement for the diameter of cables and wires in most parts of the world that use the metric decimal system. Rectangular Connectors. Cold Shrink Tubing. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. Medical Grade Tubing. Start Your Quote. Other Protocols. Adhesive Lined Dual Wall Tubing. Cross-Linked Wire. Solder Termination Sleeves.

Does not leave!
You are mistaken. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.