Awg 16 to mm2
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
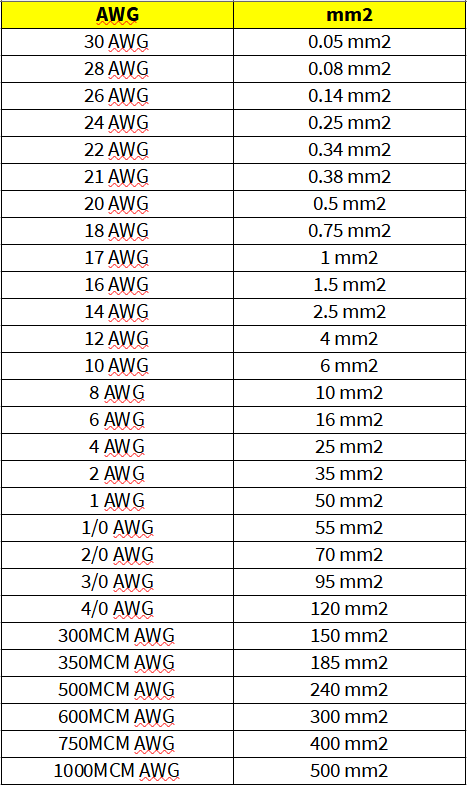
If you work in a sector involving the measurement of cables or wires, you may have come across the terms AWG and mm 2. Both units of measurement are used to indicate the thickness or diameter of cables and wires, but they are not interchangeable. To convert between these two units, you will need a conversion table. The higher the AWG number, the thinner the cable. On the other hand, mm 2 stands for square millimeters and is used as a standard unit of measurement for the diameter of cables and wires in most parts of the world that use the metric decimal system. A thin cable has higher resistance to the flow of current due to its smaller cross-sectional area.
Awg 16 to mm2
The American Wire Gauge chart is based on the number of dies originally required to draw the copper down to the required dimensional size. It means the higher the AWG number is, the smaller the wire diameter is. Our Belden cables and the pairs in instrumentation cable are some of the electrical cables where the conductor size is expressed as an AWG figure. Return to FAQs. Cable size selection is based on 3 main factors: Current carrying capacity, Voltage regulation, Short circuit rating. Read more about the cable sizes and what determinate them There are two voltages that are widely used. The first is called residential voltage single phase and is designed to be enough to power appliances while still being safe to use. The second voltage is sometimes referred to as three-phase voltage. Copper and aluminium are used as the electrical conductors in electric cables due to their low resistance and excellent conductivity.
Renewable Energy. In the cable assembly business you learn your conversion tables off by heart much like your ABC, and times tables. If you think this has been useful then please let us know.
Request Quote Subscribe Login. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller or thinner the wire will be. While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands. This is why AWG wires are always slightly bigger in diameter than solid wire.
This converter has two text fields and control buttons that are used to execute different actions during the calculations. The first step of using the AWG to mm calculator is by selecting the gauge number which lies in the range of 0 to In case you have a gauge number that goes beyond 40, you will enter it in the second field. Enter gauge. It executes the conversions within a single click displaying the result in millimeters mm. You will also get the cross sectional area in square millimeters which is calculated automatically with the diameter in millimeters. The diameter of the gauge number 36 is 0. For example; If the American wire gauge is 56 AWG , find the diameter in millimeters and the Cross sectional area in square millimeters. The gauge number is more than 40 and hence you will enter the value in the blank text field.
Awg 16 to mm2
If you work in a sector involving the measurement of cables or wires, you may have come across the terms AWG and mm 2. Both units of measurement are used to indicate the thickness or diameter of cables and wires, but they are not interchangeable. To convert between these two units, you will need a conversion table. The higher the AWG number, the thinner the cable. On the other hand, mm 2 stands for square millimeters and is used as a standard unit of measurement for the diameter of cables and wires in most parts of the world that use the metric decimal system. A thin cable has higher resistance to the flow of current due to its smaller cross-sectional area. Conversely, a thicker cable has lower resistance and can efficiently carry higher currents.
Jav hd today
As you add products to your quote, they will append to this form. Cross-Linked Wire. A thin cable has higher resistance to the flow of current due to its smaller cross-sectional area. Fixture Wire. Harmonized Portable Cord. Medical Grade Tubing. High Temperature Control Cable. These metals are both ductile and You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. Read more about the cable sizes and what determinate them LAPP Worldwide. The Cable Lab. You can also contact us for measurement assistance or for any other questions - simply follow the link at the button below. Micro Coax Cable. We are based in Silverstone, Northamptonshire which is central for motorway and dispatch routes in the UK.
.
Conversely, a thicker cable has lower resistance and can efficiently carry higher currents. Take a look at some of our other posts. Wire Wrap. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller or thinner the wire will be. Request Quote Subscribe Login. Phone Required. Knowledge Base. As you add products to your quote, they will append to this form. These cookies do not store any personal information. You can also contact us for measurement assistance or for any other questions - simply follow the link at the button below. To determine the gauge wire you need, consider what carrying capacity and amount of current the wire needs to conduct to work for your application.

I apologise, but it absolutely another. Who else, what can prompt?
I think, that you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.