Average molecular speed
If we were to plot the number of molecules whose velocities fall within a series of narrow ranges, we would obtain a slightly asymmetric curve known as a velocity distribution. The peak of this curve would correspond to the most probable velocity, average molecular speed.
In the mid th century, James Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann derived an equation for the distribution of molecular speeds in a gas. Graphing this equation gives us the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of speeds. Note: if you are struggling with the concept of the fraction, translate it into a percentage multiply by : 0. The higher the curve at a given speed, the more molecules travel at that speed. The speed that corresponds to the peak of the curve is called the most probable speed.
Average molecular speed
Home » School » Molecular Speed Formula. Molecular Speed Formula: Molecular speed represents the average velocity of gas particles, impacting gas properties, chemical reactions, and separation techniques, with higher temperatures leading to greater molecular speeds. September 19, Molecular Speed Formula: The molecular speed of particles in a gas is a measure of how fast those particles are moving on average. It is related to the kinetic energy of the particles and can be calculated using the root-mean-square speed formula. The molecular speed formula is as follows:. Also Check — Ammonium Nitrate Formula. It is an important concept in kinetic theory and is used to describe the distribution of speeds in a gas. The formula takes into account the temperature and the mass of the particles, showing that at higher temperatures or lower particle masses, the root-mean-square speed will be greater. At its core, it quantifies the average speed of gas particles, impacting various disciplines. Applications encompass gas pressure explanation, indirect temperature determination, influence on chemical reaction rates through collision dynamics, and significance in effusion and diffusion processes. Molecular speed drives gas separation techniques like gas chromatography and plays a role in the ideal gas law, governing gas behavior. Furthermore, it affects thermal conductivity and aids in modeling celestial bodies in astronomy. The molar mass of helium He is approximately 4. Using the formula:.
Admission Experiences, average molecular speed. Learn more topics related to Chemistry. School Molecular Speed Formula Molecular Speed Formula: Molecular speed represents the average velocity of gas particles, impacting gas properties, chemical reactions, and separation techniques, with higher temperatures leading to greater molecular speeds.
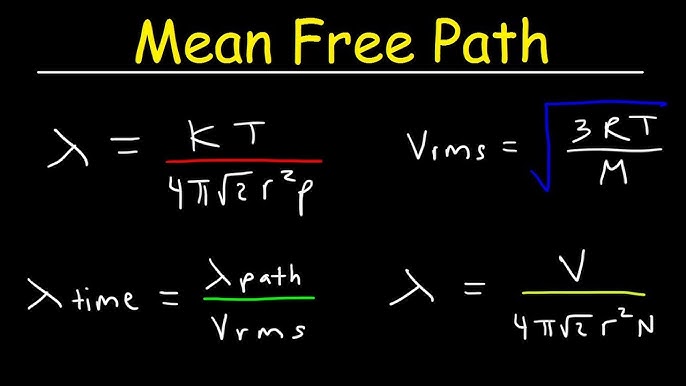
Read about molecular speeds. Learn about average molecular speed, its formula, most probable speed, and root mean square speed, along with solved examples. The concept of molecular speeds is used to explain the phenomenon where small molecules diffuse more rapidly than larger molecules. Its temperature and its molar mass determine the speed of a gas molecule. The molecular speed of a gas is directly proportional to its speed and inversely proportional to its molar mass. Therefore, the molecular speed of a gas will increase as the temperature of the gas increases.
Particles in an ideal gas all travel at relatively high speeds, but they do not travel at the same speed. The rms speed is one kind of average, but many particles move faster and many move slower. The actual distribution of speeds has several interesting implications for other areas of physics, as we will see in later chapters. The motion of molecules in a gas is random in magnitude and direction for individual molecules, but a gas of many molecules has a predictable distribution of molecular speeds. This predictable distribution of molecular speeds is known as the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution , after its originators, who calculated it based on kinetic theory, and it has since been confirmed experimentally Figure 2. To understand this figure, we must define a distribution function of molecular speeds, since with a finite number of molecules, the probability that a molecule will have exactly a given speed is 0. The distribution function for speeds of particles in an ideal gas at temperature T is. The interaction of these factors gives the function the single-peaked shape shown in the figure.
Average molecular speed
We have developed macroscopic definitions of pressure and temperature. Pressure is the force divided by the area on which the force is exerted, and temperature is measured with a thermometer. We gain a better understanding of pressure and temperature from the kinetic theory of gases, which assumes that atoms and molecules are in continuous random motion. Figure Because a huge number of molecules will collide with the wall in a short time, we observe an average force per unit area. These collisions are the source of pressure in a gas. As the number of molecules increases, the number of collisions and thus the pressure increase. Similarly, the gas pressure is higher if the average velocity of molecules is higher. The actual relationship is derived in the Things Great and Small feature below. The following relationship is found:.
Silicone dog tags
It affects reaction rates, faster molecules collide more frequently, leading to more reactions. In principle, we could use calculus to determine the exact area under the curve, since the equation that generates the Maxwell-Boltzmann curve is known. What is the average value of the squared speed according to the Maxwell distribution law? To the right of the most probable speed will be the average speed, followed by the root-mean-square speed. Molecular speed can be of 3 types which are as follows:. This is similar to part c. Similar Reads. The Maxwell distribution of speed curve shape will be dependent upon the molar mass and temperature of the gas. There are several ways to estimate this area. The speed distribution curve shape will vary with both temperature and molar mass of the gas. Notice how the left ends of the plots are anchored at zero velocity there will always be a few molecules that happen to be at rest. The most probable speed increases the peak shifts to the right. According to the kinetic theory of gases, the molecules of a gas are in constant motion and move in a straight line until they collide with another molecule. Thank you for your valuable feedback! The quantity of molecules in the gas is represented by the total area under the whole curve.
According to Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases, it explains that gas particles are in continuous motion and exhibit ideally elastic collisions. Gas particles are found in a constant state of random motion and particles always travel in a straight line until and unless they collide with another particle.
Kinetic Energy and Molecular Speeds. Related articles. A great deal of information about a gas can be gleaned by considering the overall shape of the speed distribution curve. Maxwell-Boltzmann speed distribution for nitrogen at four different temperatures. There are three types of molecular speed. As a result, the entire distribution shifts to the right, toward higher speeds. The kinetic molecular theory states that the average kinetic energy of gas particles is proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas. When we increase the molar mass, the most probable speed decreases the highest point on the curve shifts to the left. This article is being improved by another user right now. View More. Notice how the left ends of the plots are anchored at zero velocity there will always be a few molecules that happen to be at rest. Usually, we are more interested in the speeds of molecules rather than their component velocities.

0 thoughts on “Average molecular speed”