Arcuate nucleus
The hypothalamus is part of the diencephalon and has several nuclei, one of which is the arcuate nucleus. The arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus ARH consists of neuroendocrine neurons and centrally-projecting neurons. Keywords : Arcuate nucleus, Hypothalamus, Metabolic disease, Central nervous system disease, arcuate nucleus, Obesity.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The central nervous system CNS receives information from afferent neurons, circulating hormones, and absorbed nutrients and integrates this information to orchestrate the actions of the neuroendocrine and autonomic nervous systems in maintaining systemic metabolic homeostasis. Particularly the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus ARC is of pivotal importance for primary sensing of adiposity signals, such as leptin and insulin, and circulating nutrients, such as glucose. Importantly, energy state—sensing neurons in the ARC not only regulate feeding but at the same time control multiple physiological functions, such as glucose homeostasis, blood pressure, and innate immune responses. These findings have defined them as master regulators, which adapt integrative physiology to the energy state of the organism.
Arcuate nucleus
In the medulla oblongata , the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei. They receive fibers from the corticospinal tract and send their axons through the anterior external arcuate fibers and medullary striae to the cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate. This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. Download as PDF Printable version. This article is about the structure in the medulla oblongata. For the hypothalamic structure, see Arcuate nucleus. Transverse section of medulla oblongata below the middle of the olive. Dissection of brain-stem.
AgRP is an orexigenic peptide consisting of amino acids — its mature form has amino acids [ 17 ], arcuate nucleus. Critical role for peptide YY in protein-mediated satiation and body-weight regulation.
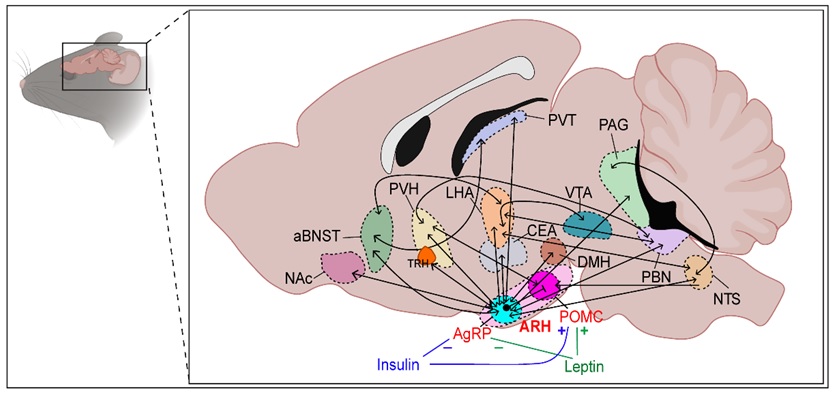
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus also known as ARH , [1] ARC , [2] or infundibular nucleus [2] [3] is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus , adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region. The arcuate nucleus provides many physiological roles involved in feeding, metabolism, fertility, and cardiovascular regulation. Groups of neuroendocrine neurons include:.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Matthew H. Bear ; Vamsi Reddy ; Pradeep C. Authors Matthew H. Bear 1 ; Vamsi Reddy 2 ; Pradeep C. Bollu 3.
Arcuate nucleus
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 10 March Despite the crucial physiological processes governed by neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus ARC , such as growth, reproduction and energy homeostasis, the developmental pathways and regulators for ARC neurons remain understudied. These markers include transcription factors whose expression is enriched in specific neuronal types and often depleted in other closely-related neuronal types, raising the possibility that these transcription factors play important roles in the fate commitment or differentiation of specific ARC neuronal types.
Nosotros los guapos online hd
Dahlstroem A, Fuxe K Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. Critical role for peptide YY in protein-mediated satiation and body-weight regulation. J Neuroendocrinol AgRP neurons can increase food intake during conditions of appetite suppression and inhibit anorexigenic parabrachial neurons. Science Terminologia Anatomica. Collectively, while tanycytes exert a clear regulatory function in control of ARC neurocircuitries, the specific role and mechanisms of tanycyte-dependent regulation of leptin action awaits further clarifications. PMID Leptin signaling in astrocytes regulates hypothalamic neuronal circuits and feeding. The primary structure of human GHRH was elucidated in [ 71 , 72 ]. Toggle limited content width. These findings include the dynamic regulation of these neurocircuits in response to sensory food perception, nutrient-induced regulation via vagal afferents and ultimately via long-term homeostatic feedback hormonal signals. S2CID
In the medulla oblongata , the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids.
In this context, the central nervous system CNS plays a pivotal role in sensing and controlling metabolic homeostasis of the organism. This apparent discrepancy in the phenotype of mice lacking the Lepr in AgRP neurons throughout development and with inducible inactivation of the same gene in adult mice highlights the importance of carefully interpreting findings from gene inactivation studies. POMC neurons regulate food intake and energy expenditure by responding to circulating blood glucose levels [ , ]. Contents move to sidebar hide. Their appetite-enhancing effects might be mediated via suppressing hypothalamic POMC neuronal activity The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. Interactions of distinct neuronal populations embedded in complex neuronal circuits monitor the internal state and provide tight homeostatic control of not only food intake and body weight, but also glucose metabolism, thirst, and blood pressure. Hum Mutat Conclusion and Outlook The hypothalamus integrates neuroendocrine and autonomic systems and coordinates metabolic responses across multiple tissues. Probably the region studied in greatest detail comprises the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus ARC. J Natl Cancer Inst J Biol Chem A decrease in blood glucose levels during fasting alters the structural organization of the blood-hypothalamus barrier in a vascular endothelial growth factor—dependent manner, thereby modulating the access of blood-borne metabolic substrates to the ventromedial ARC Palatability can drive feeding independent of AgRP neurons. Glucose sensing by POMC neurons regulates glucose homeostasis and is impaired in obesity.

0 thoughts on “Arcuate nucleus”