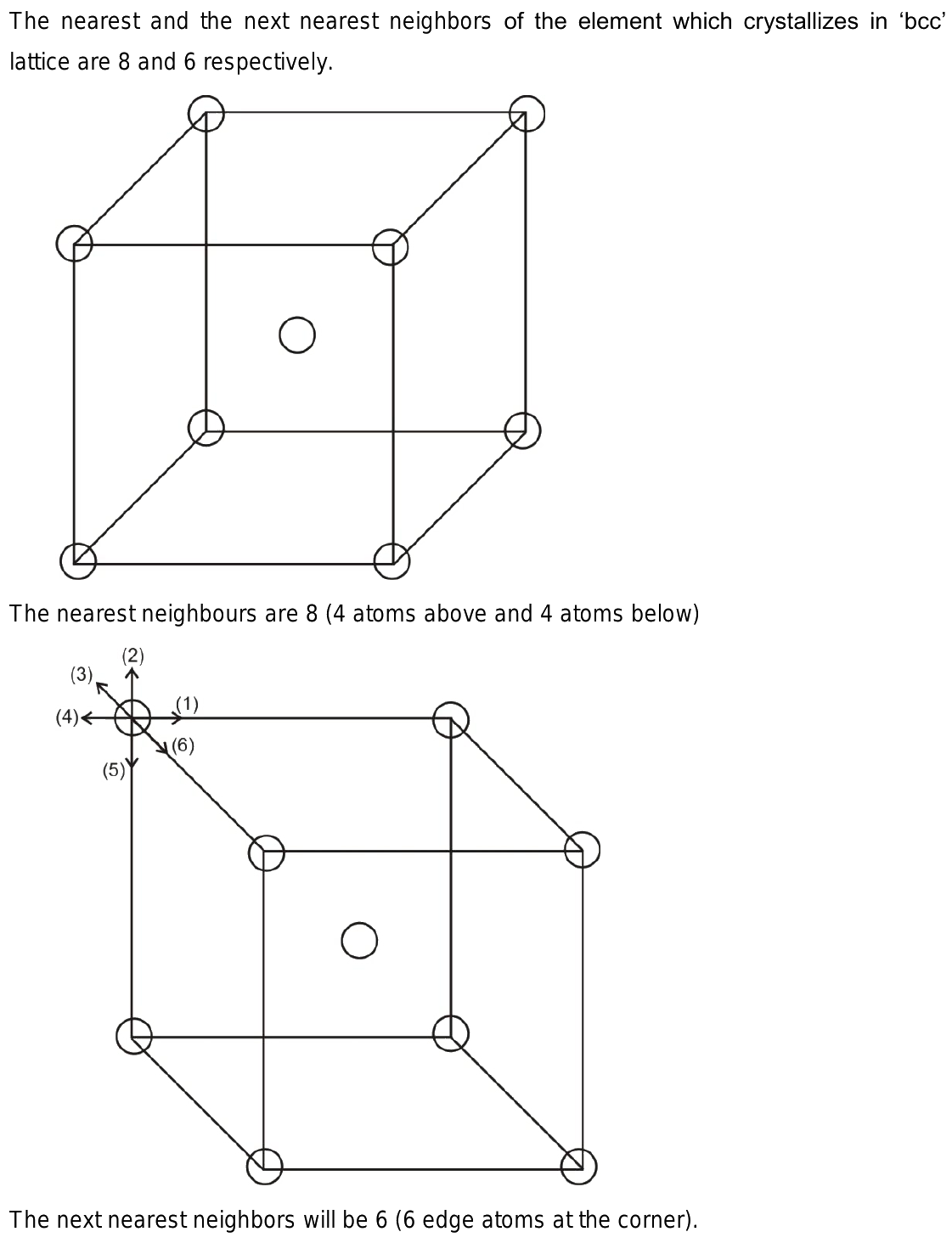
An element crystallizes in bcc structure
As element cystallises in BCC structure.
An element crystallizes in a b. The density of the element is 7. How many atoms are present in g of the element? CBSE Class 12 physics board exam today; values of physical constants, weightage. Dont't have an account? Register Now.
An element crystallizes in bcc structure
Courses for Kids. Free study material. Offline Centres. Talk to our experts An element crystallizes in bcc structure. The edge length of its unit cell is pm. If the density of the crystal is 7. Last updated date: 07th Mar Study Material. Important Questions. Chapter Pages. Revision Notes.
Courses for Kids. Competition Change.
Lithium crystallizes in a body centred cubic lattice. How many next-nearest neighbours does each Li have? An element crystallises in a f. Calculate the density if g of this element contain 2. A metal crystallises in b.
Most solids form with a regular arrangement of their particles because the overall attractive interactions between particles are maximized, and the total intermolecular energy is minimized, when the particles pack in the most efficient manner. The regular arrangement at an atomic level is often reflected at a macroscopic level. In this module, we will explore some of the details about the structures of metallic and ionic crystalline solids, and learn how these structures are determined experimentally. We will begin our discussion of crystalline solids by considering elemental metals, which are relatively simple because each contains only one type of atom. A pure metal is a crystalline solid with metal atoms packed closely together in a repeating pattern. Some of the properties of metals in general, such as their malleability and ductility, are largely due to having identical atoms arranged in a regular pattern. The different properties of one metal compared to another partially depend on the sizes of their atoms and the specifics of their spatial arrangements. We will explore the similarities and differences of four of the most common metal crystal geometries in the sections that follow. The structure of a crystalline solid, whether a metal or not, is best described by considering its simplest repeating unit, which is referred to as its unit cell. The unit cell consists of lattice points that represent the locations of atoms or ions.
An element crystallizes in bcc structure
Most solids form with a regular arrangement of their particles because the overall attractive interactions between particles are maximized, and the total intermolecular energy is minimized, when the particles pack in the most efficient manner. The regular arrangement at an atomic level is often reflected at a macroscopic level. In this module, we will explore some of the details about the structures of metallic and ionic crystalline solids, and learn how these structures are determined experimentally. We will begin our discussion of crystalline solids by considering elemental metals, which are relatively simple because each contains only one type of atom. A pure metal is a crystalline solid with metal atoms packed closely together in a repeating pattern. Some of the properties of metals in general, such as their malleability and ductility, are largely due to having identical atoms arranged in a regular pattern. The different properties of one metal compared to another partially depend on the sizes of their atoms and the specifics of their spatial arrangements. We will explore the similarities and differences of four of the most common metal crystal geometries in the sections that follow. The structure of a crystalline solid, whether a metal or not, is best described by considering its simplest repeating unit, which is referred to as its unit cell. The unit cell consists of lattice points that represent the locations of atoms or ions.
Alexa breit nude
Answer the following. A compound formed by elements A and B crystallises in cubic structure The distance of Thus , these 6 atoms are the next nearest neighbours. View Solution. Dont't have an account? Free study material. JEE Main Cutoff. Question Answers. In solid ammonia, each NH 3 molecule has six other NH 3 molecules as Exam Centres. Learn Change. Ask Now. Recently Updated Pages. Com Master of Commerce M.
Let us discuss these Principal Metallic Crystal Structures in detail. A unit cell is a building block of the Crystal structure.
Nearest and next nearest A metal has bcc structure and the edge length of its unit cell is 3. The length of the unit cell is pm. As element cystallises in BCC structure. The edge length of its unit cell is pm. Quick Link BDes M. Post Answer. Welcome Back : To keep connected with us please login with your personal information by phone. Correction Window. Pharma M. Nearest and next nearest neighbours are respectively A 8,8. I am already a member. JEE Advanced Syllabus.

I am final, I am sorry, but, in my opinion, this theme is not so actual.
It is very a pity to me, I can help nothing to you. I think, you will find the correct decision.
Instead of criticism write the variants is better.